Breaking Into Tech: How 3D Modeling Skills Can Shape Your Career Path
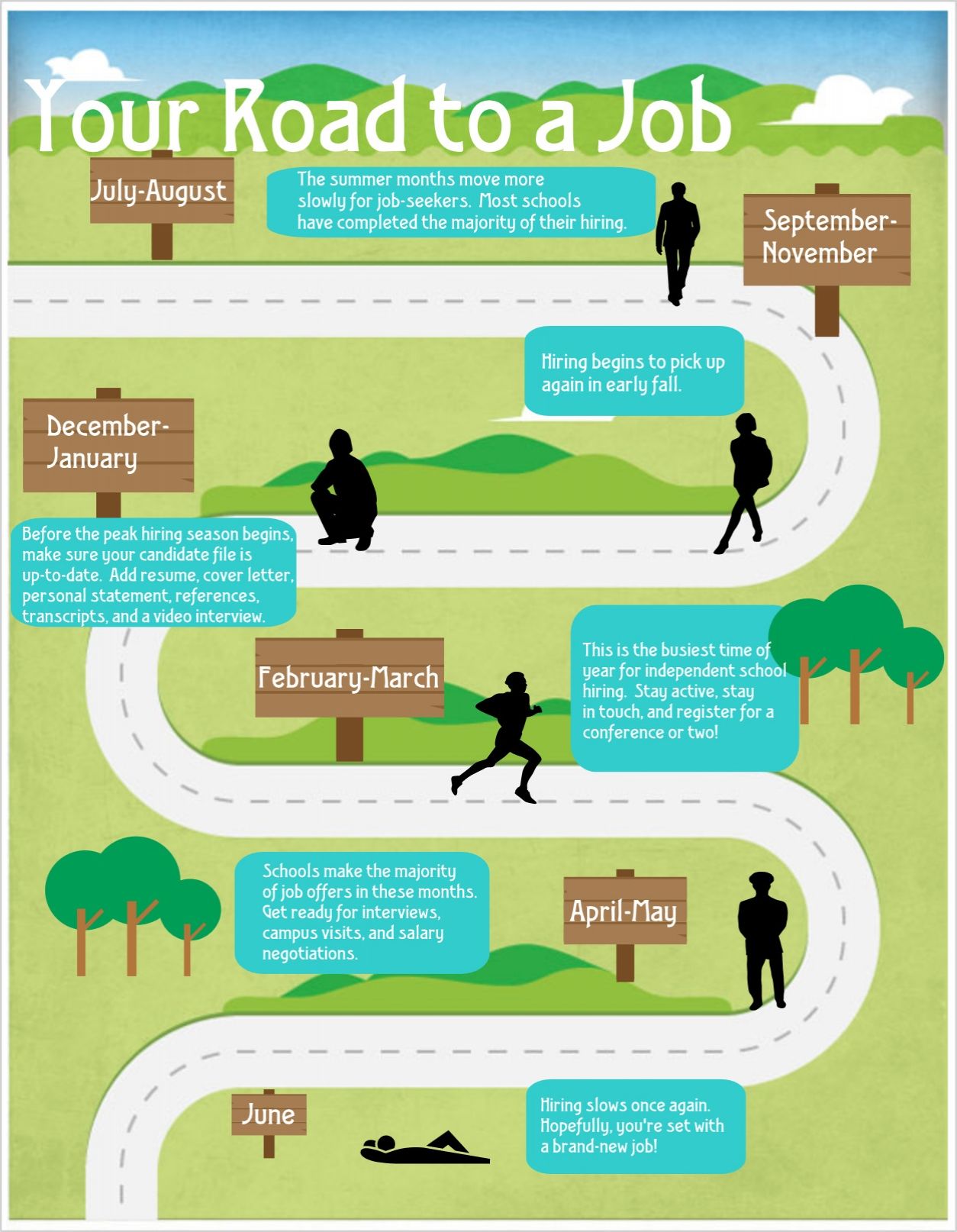
Start your tech career journey
The technology sector continues to offer some of the virtually dynamic and considerably compensate career opportunities available. Whether you’re a recent graduate, mid career professional consider a pivot, or curious about tech pathways, understand how specialized skills like 3d modeling fit into the broader landscape can give you a significant advantage.
Break into tech require a combination of target education, practical skills’ development, and strategic networking. Let’s explore how to begin this journey and specifically examine how 3d modeling expertise can open doors to specialized roles.
Foundations for a tech career
Assess your current skills and interests
Before diving into specific technical training, take inventory of your exist skills and genuine interests. The tech industry encompass countless specializations, from data science to user experience design, software development to network security. Your success and satisfaction will mostly will depend on find the intersection between market demand and your personal aptitudes.
Ask yourself these questions:
- Do you enjoy solve visual and spatial problems?
- Do you draw to creative work that combine artistic sensibility with technical precision?
- Do you find satisfaction in build digital objects or environments?
- Are you interested in how things look, function, or interact in digital spaces?
If you answer yes to several of these questions, role that leverage 3d modeling skills might align advantageously with your natural inclinations.
Research growth areas in tech
The technology sector evolves quickly. Before commit to a specific educational path, research which specializations show strong growth projections and sustainable demand. Presently, areas utilize 3d modeling skills — such as augmented reality, virtual reality, game development, and various simulation technologies — demonstrate robust growth trajectories.
Develop a learning strategy
Tech careers typically require a mix of formal education and self direct learning. Consider whether a traditional degree, bootcamp, certification program, or self pace online courses comfortably match your learning style, financial situation, and time constraints.
For 3d modeling specifically, many professionals successfully enter the field through target certification programs combine with a strong portfolio of personal projects.
Career paths enhance by 3d modeling skills
Game development
The gaming industry represent one of the virtually established career paths for those with 3d modeling expertise. Game developers create immersive digital worlds that require detailed models of characters, environments, objects, and animations.
Relevant roles:
- 3d character artist Specializes in create detailed models of game characters, focus on anatomy, expression, and movement mechanics.
- Environment artist Builds the worlds and settings where gameplay occur, from natural landscapes to futuristic cities.
- Technical artist Bridges the gap between artistic design and technical implementation, ensure models function decently within game engines.
- Prop artist Create the countless objects that populate game environments, from weapons to furniture to vehicles.
Game development studios typically look for candidates with proficiency in industry standard software like Maya, blender, or brush, along with an understanding of game engines such as unity or unreal.
Architecture and design visualization
Architectural firms progressively rely on 3d modeling to create realistic visualizations of buildings and spaces before construction begin. This field combine technical precision with aesthetic sensibility.
Relevant roles:
- Architectural visualizer Create photorealistic renderings of architectural designs for client presentations and marketing materials.
- BIM (building information modeling )specialist Develop detailed 3d models that include not precisely visual elements but besides structural, mechanical, and material information.
- Virtual reality architect Create immersive VR experiences allow clients to near walk through propose buildings.
These roles typically require proficiency in software like refit, ketchup, 3ds max, or specialized architectural visualization tools.
Film and animation
The entertainment industry employ 3d modelers to create everything from full animate features to special effects in live action films.
Relevant roles:
- Character modeler Specializes in create detailed digital characters with complex movement capabilities.
- Environment modeler Builds digital sets and landscapes for animate films or visual effects sequences.
- Visual effects (vVFX)artist Create realistic digital elements that integrate with live action footage.
- Texture artist Focus on create the surface details that make 3d models look realistic and tactile.
These positions typically require advanced skills in Maya, cinema 4d, Houdini, or similar software, along with a strong understanding of animation principles and visual storytelling.
Product design and manufacturing
Many industries use 3d modeling for product development, prototyping, and manufacturing processes.
Relevant roles:
- Product designer Uses 3d modeling to conceptualize and refine product designs before physical prototyping.
- Cad (computer aided design )specialist Create precise technical models use in manufacturing processes.
- Rapid prototyping engineer Specializes in create 3d models optimize for 3d printing and other rapid prototyping technologies.
These roles typically require proficiency in parametric modeling software like SolidWorks, fusion 360, or AutoCAD, along with an understanding of manufacturing processes.
Augmented and virtual reality development
As AR and VR technologies mature, demand for skilled 3d modelers who can create content for these immersive platforms continue to grow.
Relevant roles:
- Ar / VR content developer Create 3d assets optimize for real time rendering in AR / VR applications.
- Immersive experience designer Designs interactive 3d environments for educational, entertainment, or commercial applications.
- Medical visualization specialist Create detailed anatomical models for medical training and surgical planning in VR.
These positions typically require skills in real time 3d engines like unity or Unreal Engine, along with an understanding of the unique constraints of AR / VR platforms.
Scientific and medical visualization
Research institutions and medical facilities use 3d modeling to visualize complex data and anatomical structures.
Relevant roles:
- Medical illustrator Create detailed 3d models of anatomical structures for educational or clinical purposes.
- Scientific visualization specialist Transform complex scientific data into comprehensible 3d visualizations.
- Forensic reconstructionist Uses 3d modeling to recreate crime scenes or accidents for investigative purposes.
These specialized roles oftentimes require domain specific knowledge alongside 3d modeling skills.
Acquire 3d modeling skills
Formal education options
Several educational pathways can help you develop professional grade 3d modeling skills:
- Bachelor’s degrees Programs in computer animation, game design, digital media, or industrial design oftentimes include substantial 3d modeling components.
- Associate degrees Two year programs focus on 3d animation or digital design can provide foundational skills at a lower cost than four year degrees.
- Certificate programs Specialized certificates in 3d modeling, oft offer by art schools or technical colleges, provide focused training without general education requirements.
- Boot camps Intensive, short term programs that teach practical 3d modeling skills for specific industries like game development or architectural visualization.
Self-directed learning resources
Many successful 3d modelers are partly or alone self-teach use resources such as:
- Online course platforms Sites like Udemy, Coursera, and LinkedIn learning offer comprehensive 3d modeling courses for various software packages and specializations.
- YouTube tutorials Free, detailed tutorials cover about every aspect of 3d modeling are pronto available.
- Industry forums Communities like polycount, blender artists, orcg societyy provide feedback, resources, and network opportunities.
- Software documentation Nearly professional 3d modeling software include extensive documentation and tutorials.
Essential software to learn
The specific software you should focus on depend moderately on your target industry, but these wide use programs provide valuable skills across multiple fields:
- Blender A powerful, free, open source 3d creation suite that has gain significant industry adoption.
- Autodesk Maya An industry standard for film, television, and game development.
- Autodesk 3ds max Wide use in architecture, product visualization, and game development.
- Brush The lead digital sculpt software, peculiarly valuable for organic modeling.
- SolidWorks or fusion 360 Parametric modeling software essential for product design and manufacturing.
- Cinema 4d Popular in motion graphics and visualization work.
Many professionals recommend start with blender due to its zero cost of entry and grow industry acceptance.
Build a competitive portfolio
Quality over quantity
For 3d modeling positions, your portfolio carries more weight than formal credentials. Focus on creata fewof high quality, finished projects preferably than numerous incomplete works. Each piece should demonstrate technical proficiency, attention to detail, and creative problem soproblem-solving
Industry specific projects
Tailor your portfolio to reflect the specific industry you’re targeted:
- For game development, include character models with proper topology for animation, environment pieces optimize for real time rendering, or props with efficient UV mapping.
- For architectural visualization, showcase photorealistic building exteriors and interiors with attention to lighting and materials.
- For product design, demonstrate functional models with precise measurements and mechanical considerations.
Process documentation
Include documentation of your workflow and problem solve approach. Employers value see your thought process, include wireframes, concept sketches, and progressive iterations. This demonstrates not simply technical skill but besides methodical work habits and attention to detail.

Source: douron.com
Technical specifications
For each portfolio piece, include relevant technical information such as polygon count, texture resolution, and software use. This demonstrates your understanding of technical constraints and optimization techniques.
Break into the industry
Entry level positions
Common entry points for those with 3d modeling skills include:
- Junior 3d artist Works under senior artists to create and refine 3d assets.
- 3d generalist Handles various aspects of 3d production quite than specialize in one area.
- Production assistant Supports the 3d team with basic modeling tasks and file management.
- Freelance 3d modeler Create assets for clients on platforms like Upwork or Fiverr to build experience.
Network strategies
The tech industry, especially creative fields like 3d modeling, oftentimes rely intemperately on personal connections for hire. Effective network strategies include:
- Attend industry conferences like digraph, gGDC((ame developers conference ))or local meetups.
- Participate in online communities specific to your target industry.
- Share work in progress and finished projects on platforms like ArtStation or Behance.
- Contribute to open source projects or game jams to collaborate with other professionals.
Continuous skill development
The 3d modeling field evolve speedily with new software, techniques, and industry standards emerge regularly. Successful professionals commit to ongoing learning done:
- Follow industry blogs and YouTube channels that demonstrate cutting edge techniques.
- Take advanced courses in specialized areas like procedural modeling or photogrammetry.
- Experiment with emerge technologies like real time ray tracing or AI assist modeling tools.
- Seek feedback from established professionals to identify areas for improvement.
Long term career growth
Specialization vs. Generalization
As your career will progress, you will face choices between deeper specialization and broader skill development. Some 3d modelers become extremely specialized experts in niches like character facial modeling or architectural materials, while others develop complementary skills in areas like animation, lighting, or programming.
Both paths can lead to advancement, with specialists oftentimes become seek after consultants and generalists move into technical direction or production management.
Leadership paths
Common leadership trajectories for experienced 3d modelers include:
- Lead artist Directs a team of 3d artists, establish visual standards and workflows.
- Art director Set the overall visual direction for projects and manage multiple art disciplines.
- Technical director Focus on develop tools and pipelines to improve efficiency and quality.
- Creative director Shapes the creative vision for entire projects or product lines.
Entrepreneurial opportunities
Many experienced 3d modelers finally pursue entrepreneurial paths such as:
- Found specialized studios focus on particular industries or techniques.
- Create and sell 3d assets on marketplaces like turbo squid orcg traderr.
- Develop plugins or tools that enhance modeling workflows.
- Create educational content through courses, books, or YouTube channels.
The future of 3d modeling careers
Several emerge technologies are expanded opportunities for those with 3d modeling skills:
- Real time rendering As real time rendering approach photorealistic quality, new applications emerge in fields from architectural visualization to virtual production.
- Extended reality (xXR) The continued growth of VR, AR, and mixed reality create demand for 3d content optimize for immersive experiences.
- Digital twins Industries progressively create detailed digital replicas of physical objects and environments for simulation and monitoring.
- 3d printing Advanced manufacturing techniques require specialized 3d modeling skills to create printable designs.
- Ai assist modeling New tools use artificial intelligence to automate aspects of the 3d modeling process, change workflows and create new specializations.
Conclusion
A career leverage 3d modeling skills offer remarkable versatility across multiple industries. From create immersive game worlds to design tomorrow’s products, visualize scientific data to bring film characters to life, these skills open doors to both creative fulfillment and professional advancement.
The journey begin with honest self assessment, continue through target skill development, and flourish through consistent portfolio building and professional networking. While the learning curve can be steep, the combination of technical challenge and creative expression make 3d model an especially rewarding specialization within the broader tech landscape.

Source: architectuul.com
By strategically develop your skills in alignment with industry needs and your personal strengths, you can build a sustainable, evolve career that remain in demand level as technology continue to transform.
MORE FROM grabjobtoday.com